World Tobacco Development Report 2022
In 2022, the world witnessed a significant slowdown in economic growth, escalating geopolitical issues, and increasingly stringent tobacco control measures. The global tobacco industry sought to develop amidst this complex and ever-changing environment. Overall, tobacco consumption worldwide (excluding mainland China) remained stable. Legal cigarette sales saw a slight decline to 55.167 million cases, while the illegal cigarette trade experienced significant growth. The growth rate of heated cigarettes declined, but the sales of electronic cigarettes showed a rebound. Tobacco leaf production remained stable, with a total output of 1.742 million tons (34.84 million quintals). Brazil and the United States saw a significant decrease in production, leading to an overall increase in tobacco leaf prices and improved performance for the two major tobacco leaf companies.
Development Environment
In 2022, factors such as prolonged and recurrent outbreaks of the pandemic, escalating geopolitical conflicts, declining economic growth, and continuously escalating tobacco control measures had a profound impact on the development of the global tobacco industry.
- World Economy
The global economy experienced a significant slowdown. In 2022, the three major economies, the United States, China, and the European Union, achieved GDPs of $25.5 trillion, $18.1 trillion, and $16.6 trillion, respectively, with year-on-year growth rates of 2.1%, 3.0%, and 3.5%. In comparison, during the same period in 2021, the GDP growth rates of these three major economies were 5.9%, 8.1%, and 5.3%, respectively. Additionally, due to the significant devaluation of non-U.S. currencies against the U.S. dollar in 2022, many countries and regions experienced a rise in GDP when measured in local currency but a significant decline when measured in U.S. dollars.
- Record High Inflation
Inflation levels reached record highs. The inflation rate in the United States began to rise steadily from March 2021 and reached a peak of 9.1% in June 2022, the highest in nearly forty years. The monthly inflation rate in the European Union soared from 5.6% in January to 11.5% in October, setting a historical record. The inflation situations in some emerging economies such as Turkey, Argentina, and Russia deteriorated sharply. High inflation eroded the purchasing power of ordinary people and further weakened economic growth momentum.
- Risks from Rapid Interest Rate Hikes
High inflation forced major economies worldwide to implement significant interest rate hikes amid sluggish economic trends. The Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank raised interest rates multiple times. The contractionary policies implemented by developed economies threatened the stability of the banking industry and the broader financial sector. These policies not only had adverse effects on their own economic development but also made the fundamentals of emerging markets and developing economies more fragile. They faced severe impacts such as significant currency devaluation, continuous capital outflows, and financial market volatility.
Ukraine Crisis
- Soaring Production and Living Costs
Commodity prices fluctuated dramatically, with significant increases in energy and raw material prices. Employees demanded wage increases to cope with inflation, leading to rising production and operating costs for businesses, squeezing their profit margins. Additionally, reduced disposable income and deteriorating future expectations for consumers had negative effects on various industries, including the tobacco industry.
- Disruption of Ongoing Business Operations
The war triggered by the Ukraine crisis posed a direct threat to local production and business activities and the safety of personnel. Financial and economic sanctions forced companies to adjust their operations, disrupting the global industrial layout and further impacting the global supply chains that were already severely affected by the pandemic.
- Widespread Impact of Tobacco-related Sanctions
The United States, the European Union, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and other countries have imposed various sanctions on Russia. In response, Russia has implemented countermeasures, including restrictions on the export of tobacco-related production equipment. Major multinational tobacco companies announced a temporary suspension of their operations in Russia following the crisis. They continued to assess operational risks and losses, including concerns about possible retaliatory actions by Russia, the possibility of nationalizing foreign companies or assets, and taking legal actions against employees. These companies sought to divest assets and business operations in Russia. The Ukraine crisis also led to a sharp increase in the sales of illicit tobacco products in the region. Investigations showed that about one-fourth of Russians had turned to the consumption of illegal cigarettes.
Tobacco Regulation
- World Health Organization
In 2022, the number of parties to the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control remained unchanged at 182, covering over 90% of the world’s population. The Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products received ratification from Moldova and Paraguay, bringing the total number of parties to 66. The “Investment Fund,” established by the previous Conference of the Parties, officially began its operations. The World Bank acts as the trustee of the fund and the interest earned will be used to support tobacco control activities of the parties. The theme of the 35th World No Tobacco Day was “Tobacco Threatens the Environment,” linking tobacco consumption to environmental protection. Governments were urged to be vigilant against tobacco companies’ high-profile promotion of sustainable development and obtaining ESG rankings. The World Health Organization refused to include Medicago’s tobacco plant-based COVID-19 vaccine in the emergency use approval list due to the violation of its policy by FEMO International, which holds a one-third stake in Medicago. However, the World Health Organization also indicated that it might reassess its policy as the tobacco industry attempts to enter other product categories, and discuss how to address the overall trend of the tobacco industry investing in the health sector.
- World Customs Organization
The new customs codes for novel tobacco products came into effect on January 1, 2022. By December 2022, 94 out of 160 contracting parties to the World Customs Organization’s Harmonized System Convention, including the European Union and the United States, had notified the organization of their implementation of the 2022 version of the Harmonized System, creating new dedicated customs codes for novel tobacco and nicotine-containing products.
- United States
In 2022, tobacco regulations in the United States faced various controversies and lawsuits. After multiple court orders to delay the implementation of rules requiring pictorial health warnings on cigarette packaging, the court declared the rule unconstitutional in December 2022. The judge stated that there was no evidence that such graphic warnings reduced smoking rates, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may appeal to the Federal Appeals Court. The FDA gained regulatory authority over synthetic nicotine and synthetic nicotine products that were not granted market authorization and cannot continue to be sold in the U.S. market after July 13, 2022. The FDA strengthened flavor bans and proposed product standards for menthol in cigarettes and flavor characteristics in cigars, intending to prohibit the sale of menthol cigarettes and flavored cigars in the United States. The FDA plans to establish maximum nicotine levels for combustible tobacco products, lowering nicotine levels to a “minimum or non-addictive” level.
- European Union
Regulatory law revisions are being advanced in the European Union. The European Commission is revising the Tobacco Excise Directive (TED), which may include the definition and tax treatment of novel tobacco and nicotine-containing products, including heated cigarettes, electronic cigarettes, and nicotine pouches. After several delays, the proposal is expected to be adopted by the European Commission in the first half of 2023 and by the European Council in 2024. Preparations are also underway for the revision of the Tobacco Products Directive (TPD), which is expected to be adopted by 2025. On November 23, 2022, the European Commission issued an implementing directive that requires all EU member states to apply the directive from October 23, 2023, banning the use of special flavors in heated cigarettes in the European Union. This will have a significant impact on a large portion of novel tobacco products currently sold in the EU.
- Other
For example, New Zealand passed an amendment to its smoke-free environment legislation in 2022, targeting smoke-emitting tobacco products (combustible tobacco products). Japan’s ruling party formulated a new tax reform outline. Mexico banned the import and export trade of heated cigarettes and electronic cigarettes and implemented regulations under the Tobacco Control Law.
Various Tobacco Products
In 2022, as COVID-19 control measures began to relax and socioeconomic activities gradually returned to normal, tobacco consumption remained relatively stable overall. According to Euromonitor International’s forecast data, global cigarette sales saw a slight decline, the growth rate of heated cigarettes declined, and the sales of electronic cigarettes rebounded.
- Cigarettes
In 2022, legal cigarette sales worldwide failed to maintain the recovery trend of the previous year and entered a downward trajectory, accompanied by a resurgence of the illegal cigarette trade.
Global legal cigarette sales reached 551.67 million cases, a year-on-year decline of 1.1%, with sales amounting to $536.67 billion, a year-on-year increase of 3.7%. Among countries and regions, 16 countries had legal cigarette sales exceeding one million cases, accounting for 60.2% of global cigarette sales. Indonesia, the United States, and Russia were the top three countries in terms of sales volume, while the top three countries in terms of sales amount were the United States, Indonesia, and Germany, accounting for 66.5% of global cigarette sales.
The global volume of illegal cigarette trade was 7.883 million cases, an 8.7% year-on-year increase. Countries with illegal cigarette trade volumes exceeding 500,000 cases included Brazil (1.106 million cases), Pakistan (710,000 cases), Russia (580,000 cases), Indonesia (555,000 cases), and India (527,000 cases). Illicit cigarettes accounted for approximately 12.5% of global cigarette consumption. Countries where illicit cigarettes accounted for more than half of local cigarette consumption included Ecuador (65.8%), Malaysia (59.9%), Uganda (59.2%), Peru (51.3%), and Bosnia and Herzegovina (50.8%).
- Cigars
In 2022, there was a divergence in sales of different types of cigars.
Global sales of regular cigars reached 12.24 billion units, a year-on-year increase of 2.9%, with sales amounting to $19.46 billion, a year-on-year increase of 8.0%. The United States was the largest consumer of regular cigars, accounting for 86.2% of global sales volume and 68.6% of sales amount. The top three companies in terms of market share were Imperial Brands (23.4%), Swisher International Group (21.3%), and Scandinavian Tobacco Group (15.9%).
Global sales of miniature cigars reached 21.93 billion units, a year-on-year decrease of 17.9%, with sales amounting to $7.03 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 5.4%. In 2022, Japan increased the tax burden on miniature cigars to match that of cigarettes, leading to a significant decline in sales. Japan’s sales volume and sales amount decreased by 42.3% and 29.3%, respectively, accounting for 29.5% and 22.0% of global sales. The top three companies in terms of market share were Japan Tobacco (22.6%), British American Tobacco (13.1%), and Scandinavian Tobacco Group (8.3%).
- Electronic Cigarettes
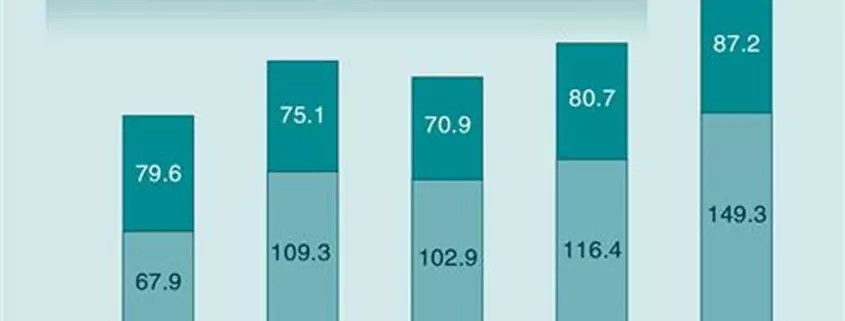
In 2022, the growth of electronic cigarettes accelerated. Global sales of electronic cigarettes reached $23.65 billion, a year-on-year increase of 20.0%. In terms of subcategories, the sales of open-system electronic cigarettes and refillable e-liquids amounted to $8.72 billion, a year-on-year increase of 8.1%, while the sales of closed-system electronic cigarettes reached $14.93 billion, a year-on-year increase of 28.2%. Cartridge-based electronic cigarettes and disposable electronic cigarettes accounted for 82.9% and 17.1% of sales, respectively. Sales of disposable electronic cigarettes reached $2.55 billion, almost doubling compared to the previous year. In terms of markets, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada ranked in the top three in terms of electronic cigarette sales, with sales amounts of $9.00 billion, $5.03 billion, and $1.98 billion, respectively. The top three companies in terms of market share were British American Tobacco, JUUL Labs, and RELX Technology, accounting for 17.4%, 14.4%, and 8.9% of global electronic cigarette sales, respectively.
- Heated Cigarettes
In 2022, sales of heated cigarettes reached $33.38 billion, a year-on-year increase of 15.8%. The sales volume of heated tobacco devices was 30 million units, with sales amounting to $2.09 billion, while the sales volume of heated tobacco sticks was 2.756 million cases, with sales amounting to $31.28 billion. Japan, Italy, and Russia ranked in the top three in terms of market sales, with sales amounts of $12.77 billion, $4.11 billion, and $2.54 billion, respectively. The growth rate of heated cigarettes in Japan continued to slow down, and its share of global sales declined from over 80% before 2017 to 38.3% in 2022. The top three companies in terms of market share were Philip Morris International (71.4%), British American Tobacco (15.5%), and Japan Tobacco (4.3%).
- Other Tobacco Products
Nicotine pouches (or modern oral nicotine products) have been the fastest-growing novel tobacco product in recent years. In 2022, sales reached 10.65 billion pouches, a year-on-year increase of 56.1%, with sales amounting to $5.33 billion, a year-on-year increase of 77.7%. However, their share in the global tobacco product sales was less than 1%, with the market primarily concentrated in the United States and the Nordic countries such as Sweden, Norway, and Denmark. Traditional oral tobacco products remained relatively stable, with sales volumes of 121,000 tons and sales amounts of $13.95 billion. Hand-rolled cigarettes and pipe tobacco maintained low growth rates, with sales volumes of 104,000 tons (equivalent to approximately 2.958 million cases of cigarettes) and 146,000 tons, a year-on-year increase of 1.9% and 2.5%, respectively. Sales amounts reached $34.39 billion and $7.93 billion, with year-on-year increases of 6.6% and 8.7%, respectively.
| Tobacco Product | Sales Volume | Sales Amount (in billions USD) | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cigarettes | 551.67 million | 536.67 | -1.1% |
| Cigars (Regular) | 12.24 billion | 19.46 | 2.9% |
| Cigars (Miniature) | 21.93 billion | 7.03 | -17.9% |
| Electronic Cigarettes | – | 23.65 | 20.0% |
| Heated Cigarettes | – | 33.38 | 15.8% |
| Nicotine Pouches | 10.65 billion | 5.33 | 56.1% |
| Oral Tobacco | – | 13.95 | – |
| Hand-Rolled Cigarettes | 104,000 tons | 34.39 | 1.9% |
| Pipe Tobacco | 146,000 tons | 7.93 | 2.5% |
News Source:
https://paper.eastobacco.com/html/2023-06/03/content_3_1.htm
- Minneapolis Sets $25 Minimum Price for E-Cigarettes - July 11, 2025
- Alabama Schools to Implement New Anti-Vaping Policies - July 11, 2025
- Is Vaping and Driving Illegal in Rhode Island? (2025 Guide) - July 10, 2025