Adult E-Cigarette Use Surges 20.3% as Cigarette Smoking Declines 5.2% from 2017 to 2023, CDC Study Reveals
A recent CDC study published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report uncovers a significant shift in adult tobacco use trends from 2017 to 2023. The prevalence of exclusive cigarette smoking declined by 5.2% (from 10.8% to 7.9%), while exclusive e-cigarette use surged by 20.3% (from 1.2% to 4.1%) during this period. These changes translate to a decrease of approximately 6.8 million exclusive cigarette smokers and an increase of approximately 7.2 million exclusive e-cigarette users.
To fully grasp the implications of these findings, let’s dive into the study’s methodology and explore the age-specific trends that contribute to this shifting landscape of tobacco product preferences.
Understanding the Study and Its Significance
The CDC researchers analyzed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), an annual cross-sectional household survey that captures information on the health and behaviors of the U.S. civilian population. The study included a substantial sample size, ranging from 21,153 to 31,997 adult participants each year between 2017 and 2023.
By assessing current use of various tobacco products, including combustible tobacco (such as cigarettes and pipes), smokeless tobacco, and e-cigarettes, the researchers were able to track overall tobacco use prevalence, as well as use by specific age groups and exclusivity of use.
These findings provide valuable insights into the evolving tobacco use patterns among U.S. adults, which can inform public health policies, resource allocation for tobacco control programs, and the development of targeted interventions to reduce the burden of tobacco-related diseases.
Age-Specific Trends: A Closer Look
The study revealed notable age-specific trends that contribute to the overall shift from cigarettes to e-cigarettes:
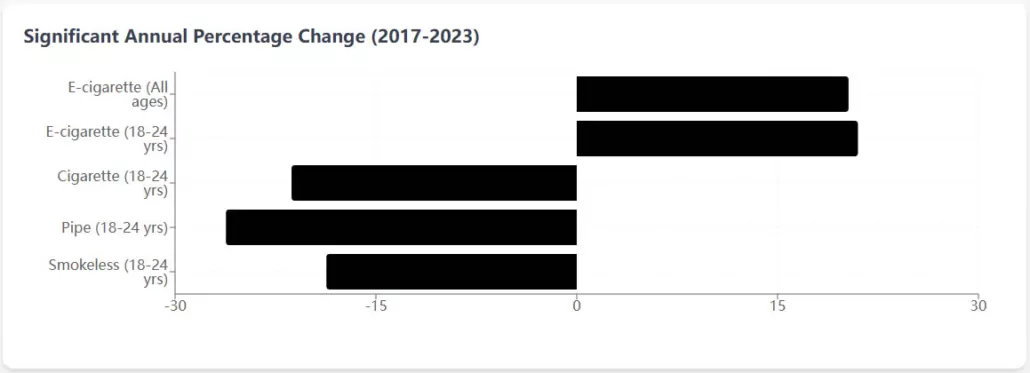
- Young Adults (18-24 years):
- Exclusive cigarette smoking decreased from 6.5% to 1.2%
- Pipe smoking decreased from 1.0% to 0.1%
- Exclusive e-cigarette use increased dramatically from 2.7% to 10.3%
- Adults (25-44 years):
- Exclusive cigarette smoking declined from 12.0% to 7.6%
- Exclusive e-cigarette use rose from 1.5% to 6.1%
- Middle-aged Adults (45-64 years):
- Exclusive e-cigarette use increased in terms of population estimates from 690,000 to 1.6 million
- Older Adults (65+ years):
- Exclusive pipe smoking decreased from 0.4% to 0.1%
- Exclusive cigarette smoking increased slightly in population estimates from 3.6 million to 4.2 million
These age-specific trends highlight the substantial increase in exclusive e-cigarette use among younger adults (18-24 and 25-44 years), indicating a potential shift in tobacco use initiation and patterns that could have long-term public health implications.
Read the full report:
Notes from the Field: Tobacco Product Use Among Adults — United States, 2017–2023
Implications for Public Health and Tobacco Control
While the decline in exclusive cigarette smoking is encouraging, the offsetting rise in exclusive e-cigarette use presents new challenges for public health and tobacco control efforts. The potential health risks of e-cigarettes, including their impact on respiratory health, cardiovascular function, and the developing brain in young adults, are not yet fully understood.
Moreover, the substantial increase in e-cigarette use among younger adults raises concerns about the potential for e-cigarettes to serve as a gateway to nicotine addiction. Young people who start using e-cigarettes may be more likely to transition to traditional cigarettes or other tobacco products in the future.
To address these evolving trends, the study’s authors emphasize the importance of continued surveillance and the use of comprehensive tobacco control strategies, such as price increases, smoke-free policies, high-impact media campaigns, and cessation support programs.
Conclusion
The CDC study provides a valuable snapshot of the changing landscape of adult tobacco use in the United States, highlighting the significant decline in exclusive cigarette smoking (5.2%) and the concurrent surge in exclusive e-cigarette use (20.3%) from 2017 to 2023. While the decrease in cigarette smoking is a positive development, the offsetting increase in e-cigarette use presents new challenges for public health and tobacco control efforts, particularly among younger adults.
As we navigate this shifting terrain, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing the potential risks associated with e-cigarette use. By implementing comprehensive tobacco control strategies, monitoring trends in tobacco product use, and promoting prevention and cessation efforts, we can work towards the ultimate goal of reducing nicotine addiction and its associated adverse health outcomes.
As individuals, we can also play a role in promoting a tobacco-free future by staying informed about the risks of all tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, and supporting policies and programs that encourage prevention and cessation. By working together at both the individual and societal levels, we can create a healthier, smoke-free future for all.
- Austria Plans to Ban Disposable E-Cigarettes - August 5, 2025
- Vaping vs. THC Drinks: Which Cannabis Option Is Right for You? - August 4, 2025
- Colombia’s New Vape Law: A Reality Check on Enforcement - August 4, 2025









