New Research: E-Cigarettes Less Harmful, Minimal Impact on Lungs
E-Cigarettes vs. Traditional Cigarettes: Comparative Analysis of Lung Health Impact
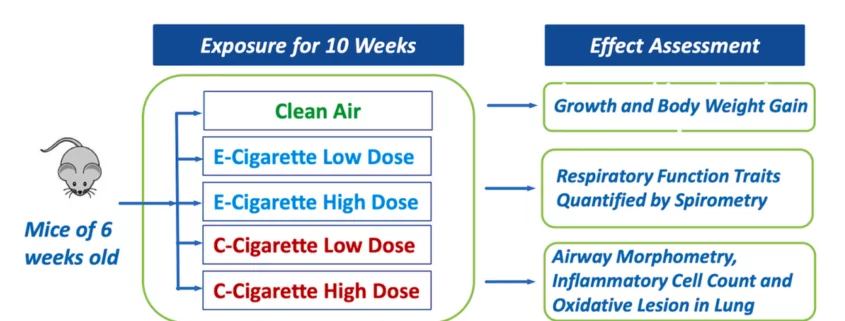
In recent research conducted by a team from Shanghai’s Tenth People’s Hospital, published in the esteemed journal Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, it was revealed that e-cigarettes have a significantly lesser impact on the lung health of young individuals when compared to traditional cigarettes. Unlike traditional cigarettes, which are known to reduce lung capacity and contribute to various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema, e-cigarettes pose minimal harm to the lungs. This groundbreaking study, supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, the National Postdoctoral Innovation Talent Program, and the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, employed animal experiments involving adolescent mice exposed to both traditional cigarettes and e-cigarettes. The researchers meticulously recorded various lung risk indicators, with lower values indicating less damage. The findings clearly demonstrated that every lung risk indicator for the e-cigarette group was significantly lower than that of the traditional cigarette group, thereby establishing the reduced harm potential of e-cigarettes.
Traditional cigarettes are widely recognized as major contributors to lung damage and respiratory diseases. They have several adverse effects on the lungs, including increased breathing resistance, decreased respiratory function, enlarged alveolar spaces leading to emphysema, and thicker airway walls resulting in COPD. These conditions severely compromise lung health and can have long-term consequences. The negative impact of smoking even a single traditional cigarette per day is evident, as it causes oxidative damage to the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs responsible for oxygen exchange. The cumulative effect of smoking over time can lead to severe lung-related ailments.
In contrast to traditional cigarettes, e-cigarettes do not induce significant pathological changes in the lungs. The research conducted on adolescent mice revealed that even light e-cigarette use, within the limits of one hour per day, showed lung health conditions almost identical to those of regular mice. This indicates that the impact of e-cigarettes on lung health is considerably lower. Furthermore, even heavy e-cigarette users exhibited less severe lung damage compared to smokers. The data gathered from the study showed that smoking just one traditional cigarette daily causes considerable oxidative damage to the alveoli, while e-cigarettes do not pose this risk. These findings strongly suggest that e-cigarettes are a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes in terms of lung health.
Numerous studies conducted in recent years have supported the notion that smokers who switch to e-cigarettes can experience improvements in their lung health. A paper published in April 2021 in The Lancet, a renowned medical journal, highlighted the effectiveness of e-cigarettes in reducing the intake of lung carcinogens among smokers who made the switch. Similarly, a study conducted by Boston University in May 2022 demonstrated that smokers who switched to e-cigarettes experienced positive enhancements in respiratory health. However, it is important to note that when e-cigarette users transitioned back to traditional cigarettes, their risk of respiratory diseases doubled. These studies emphasize the potential benefits of e-cigarettes as harm reduction products, particularly for individuals seeking to improve their lung health.
In summary, the comprehensive research conducted by the team at Shanghai’s Tenth People’s Hospital, with support from esteemed organizations, confirms that e-cigarettes have a significantly lesser impact on lung health compared to traditional cigarettes. Traditional cigarettes are known to reduce lung capacity, contribute to diseases such as COPD and emphysema, and cause substantial lung damage. Conversely, e-cigarettes do not induce significant pathological changes in the lungs, even among heavy users. Smokers who switch to e-cigarettes can potentially improve their lung health, as confirmed by various studies. It is essential to recognize the importance of thoroughly studying how e-cigarettes affect the lung health of young individuals to inform public health policies and guide individuals towards safer alternatives.
- NEXA PIX 35K Disposable Vape with Crystal Tank Review - August 15, 2025
- Baton Rouge, LA Imposes 500-Foot Buffer Zone for Vape Shop from Schools - August 15, 2025
- Alabama Vape Law Temporarily Blocked by Judge Gaines - August 15, 2025