Does Vaping Cause Hair Loss? Nicotine & Hair Health Facts
Hair loss is a common concern that touches many lives, prompting questions about its causes and potential contributing factors. From genetics to stress, various elements influence hair health. In recent years, with the rise of electronic cigarettes, a specific question frequently arises: Does vaping cause or worsen hair loss? While the image of stress-related shedding or age-related thinning is familiar, understanding how lifestyle choices like vaping might fit into the picture requires a closer look at the science of hair growth, the effects of nicotine, and the broader impacts of inhaled substances.
Let’s delve into the intricate world of hair follicles, explore the potential mechanisms by which vaping *could* theoretically impact hair health, compare it to the known effects of traditional smoking, and discuss what current research suggests – and what remains uncertain.
Understanding the Life Cycle of Your Hair
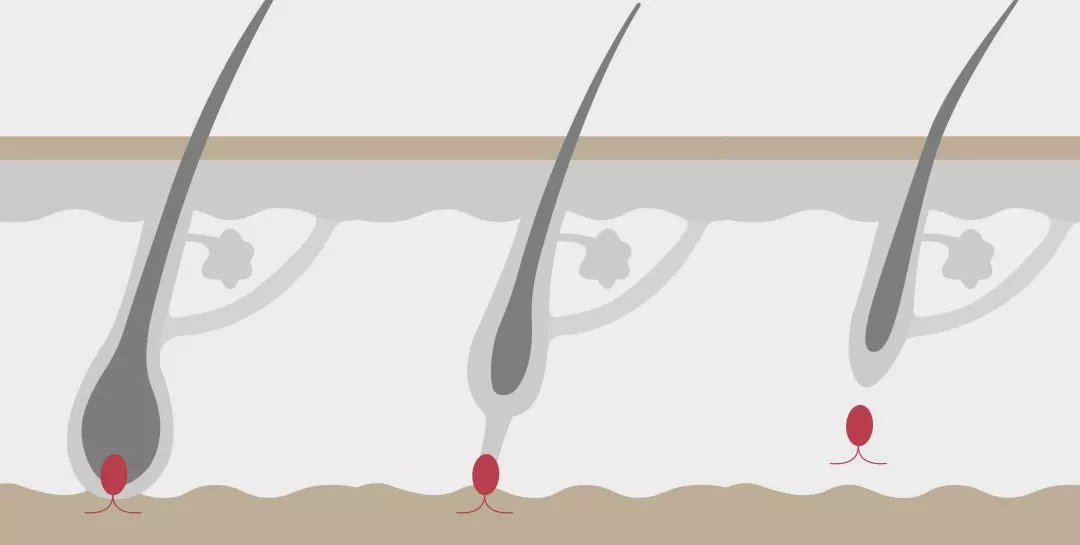
Before exploring potential disruptions, it’s helpful to understand how healthy hair normally grows. Hair doesn’t just continuously lengthen; it goes through a sophisticated, multi-phase cycle occurring within tiny structures in the skin called hair follicles. This cycle ensures hair renewal and involves three main stages:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): This is the active growth period where cells within the hair follicle divide rapidly, pushing the hair shaft upwards and outwards. This phase is the longest, typically lasting anywhere from 2 to 7 years for scalp hair, determining the maximum length your hair can reach. The vast majority (around 85-90%) of your scalp hairs are in the anagen phase at any given time.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): Following the growth phase, the hair follicle enters a short transitional stage called catagen, lasting only about 2-3 weeks. During this time, hair growth stops, the follicle shrinks slightly, and the base of the hair root detaches from its blood supply, preparing to be shed.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): This is the final resting phase, typically lasting around 3 months. The hair shaft is fully formed and inactive, resting in the follicle while a new hair begins to grow beneath it in a new anagen phase. Eventually, the resting hair is shed (we naturally lose about 50-100 telogen hairs per day), allowing the new hair to emerge. About 10-15% of scalp hairs are normally in the telogen phase.
This intricate cycle relies on a complex interplay of genetics, hormones, and adequate nourishment delivered to the follicle. Disruptions to any part of this cycle can lead to noticeable changes in hair density, texture, or increased shedding.
Fueling the Follicle: What Healthy Hair Needs
Think of each hair follicle as a tiny factory constantly working to produce hair. Like any factory, it needs fuel and the right operating conditions. Essential requirements for healthy hair growth include:
- Robust Blood Flow: Tiny blood vessels (capillaries) deliver oxygen and vital nutrients directly to the base of the hair follicle. Sufficient circulation is non-negotiable for the energy-intensive process of hair production during the anagen phase.
- Essential Nutrients: Hair is primarily made of protein (keratin), so adequate protein intake is crucial. Additionally, vitamins and minerals play vital roles. Key players include B vitamins (especially Biotin), Vitamin D, iron, zinc, and Vitamin C (which aids iron absorption and collagen production). Deficiencies in these nutrients are known causes of hair shedding or poor hair quality. You can find more information on diet and hair health from resources like the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD).
- Healthy Scalp Environment: The skin on the scalp needs to be healthy to support follicle function. Conditions like excessive inflammation, infections, or irritation can negatively impact hair growth.
- Hormonal Balance: Hormones, particularly androgens (like testosterone and its derivative dihydrotestosterone, DHT), play a significant role in regulating the hair cycle. Imbalances or sensitivity to these hormones are key factors in common types of hair loss like androgenetic alopecia.
Any factor that compromises these essential requirements can potentially disrupt the hair growth cycle and contribute to hair loss or thinning.
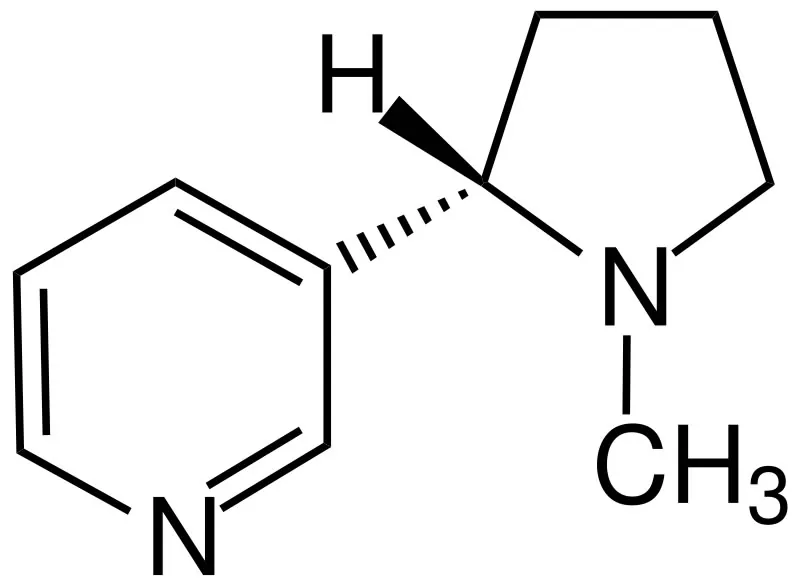
The Nicotine Connection: Constricting Blood Flow
This is where substances like nicotine enter the discussion. Nicotine, the primary addictive component in both traditional cigarettes and most vaping products, is a well-known vasoconstrictor. This means it causes blood vessels to narrow or tighten. As explained by the American Heart Association, nicotine stimulates the body to produce adrenaline, which raises blood pressure and heart rate, and constricts arteries.
How does this relate to hair? The tiny capillaries supplying the hair follicles are particularly susceptible to vasoconstriction. When these vessels narrow due to nicotine exposure, the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients to the hair follicle’s base can be reduced. Over time, this chronic reduction in blood flow could potentially starve the follicles, weakening the hair shaft, shortening the anagen (growth) phase, and possibly triggering premature entry into the telogen (resting/shedding) phase. While direct studies definitively linking nicotine-induced vasoconstriction from *vaping* specifically to hair loss are limited, the underlying physiological mechanism is plausible and well-established for nicotine absorbed through smoking.
Beyond Nicotine: Vaping Aerosols and Oxidative Stress
While nicotine is a major focus, vaping aerosols contain more than just nicotine and flavoring. They include solvents like propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin, various flavoring chemicals, and potentially trace amounts of other substances, including heavy metals shed from the heating coil. When these substances are heated and inhaled, they can contribute to **oxidative stress** within the body.
Oxidative stress occurs when there’s an imbalance between harmful molecules called free radicals and the body’s ability to counteract them with antioxidants. Free radicals can damage cells, proteins, and DNA. Research, primarily focused on smoking but increasingly looking at vaping, suggests that inhaled aerosols can increase oxidative stress markers in the body (Example study on oxidative stress markers). Hair follicle cells are metabolically active and potentially vulnerable to oxidative damage. Chronic oxidative stress could theoretically impair follicle function, contribute to inflammation around the follicle, and potentially accelerate hair aging or shedding processes. While more research specifically linking vaping-induced oxidative stress to hair loss is needed, it represents another potential biological pathway through which vaping *could* impact hair health.
Hormonal Balance and Hair: A Potential Nicotine Influence?
Hormones are critical conductors of the hair growth symphony. Androgenetic alopecia (AGA), the most common form of hair loss often referred to as male or female pattern baldness, is directly linked to genetics and the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a potent androgen derived from testosterone. Nicotine’s potential influence on the body’s hormonal balance is complex and not fully elucidated, especially concerning hair cycles.
Some research suggests smoking (which includes nicotine exposure alongside thousands of other chemicals) can influence androgen levels, but directly linking nicotine from vaping to clinically significant hormonal changes that cause hair loss is less established. It’s possible that chronic nicotine use could subtly influence the endocrine system, but whether this effect is potent enough to trigger or noticeably worsen conditions like AGA solely from vaping remains an area requiring further investigation. Genetics remain the dominant factor in AGA.
Comparing Vaping to Traditional Smoking: A Spectrum of Risk
When discussing potential health impacts, comparing vaping to smoking is crucial. The link between **traditional cigarette smoking and hair loss** is more firmly established in scientific literature. Multiple studies have associated smoking with an increased risk of developing androgenetic alopecia and potentially accelerating its progression (Review on Smoking and Hair Loss). The mechanisms are believed to be multifactorial, including:
- Severe vasoconstriction from nicotine and other smoke components.
- Massive oxidative stress from thousands of inhaled combustion byproducts.
- Potential damage to hair follicle DNA from smoke carcinogens.
- Increased inflammation.
Vaping, by eliminating combustion, removes exposure to tar and many of the most toxic chemicals found in cigarette smoke. This is why public health bodies generally consider it significantly less harmful than smoking overall. However, vaping is not harmless. It still delivers nicotine (with its vasoconstrictive effects) and introduces other chemicals into the lungs, leading to potential oxidative stress and inflammation, albeit likely at lower levels than smoking.
Therefore, while smoking poses a clearly documented and higher risk to hair health (among many other health risks), vaping cannot be considered entirely neutral. It shares the nicotine risk factor and introduces its own set of inhaled chemicals whose long-term effects on hair follicles are still under investigation.
Ecigator is one of the well-known vape brands spun off from FM Technology Co., Ltd, it’s an ISO-certified disposable vape manufacturer for OEMs, ODMs, and OBM since 2010. The founder team comes from top firms with more than 10 years of experience in the vaping industry and has devoted thousands of hours to providing users with a better and better experience.

18K Disposable Pod Kit
Disposable Pod Kit – 18ml changeable pod with 650mAh rechargeable battery.

20K with Large Screen
20000 Puffs Disposable Vape with large screen. Normal and Boost working modes.

20K DTL Disposable
20K Puffs DTL(Directly to Lung) disposable vape with airflow control and screen.
If I Stop Vaping, Will My Hair Grow Back?
This is a common and hopeful question. If vaping *is* contributing to hair thinning or loss through mechanisms like reduced blood flow or increased oxidative stress, then quitting could potentially help improve the situation. Ceasing nicotine intake allows blood vessels to relax, improving circulation to the scalp. Reducing exposure to inhaled chemicals can lower oxidative stress. This creates a healthier environment for hair follicles to function optimally.
Many people who quit smoking report perceived improvements in skin and hair health over time. Similar benefits might be experienced after quitting vaping. However, it’s crucial to manage expectations. If the primary cause of hair loss is genetic, like androgenetic alopecia, quitting vaping alone is unlikely to reverse the underlying condition or regrow hair that has been permanently lost due to follicle miniaturization. Quitting can, however, potentially slow down progression exacerbated by poor circulation or inflammation and allow existing, viable follicles to produce healthier, stronger hair. Any potential regrowth would likely be gradual, occurring over several hair cycles (months to years).
A Holistic View: Preventing and Addressing Hair Loss
It’s vital to remember that vaping or nicotine use is just one potential piece of a much larger puzzle when it comes to hair health. Many factors contribute to hair loss, including:
- Genetics: The primary driver of androgenetic alopecia.
- Age: Hair naturally thins and growth slows with age.
- Hormonal Changes: Thyroid issues, pregnancy, menopause.
- Medical Conditions: Autoimmune diseases (like alopecia areata), scalp infections.
- Medications: Certain drugs can list hair loss as a side effect.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of iron, zinc, biotin, protein, etc.
- Stress: Severe physical or emotional stress can trigger temporary shedding (telogen effluvium).
- Hair Care Practices: Harsh treatments, tight hairstyles causing traction alopecia.
Therefore, addressing hair loss effectively usually requires a holistic approach. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga, practicing gentle hair care, and avoiding known triggers (like smoking) are all beneficial steps. If you are experiencing noticeable hair loss, consulting a doctor or a dermatologist is essential to determine the underlying cause. They can diagnose the specific type of hair loss and discuss appropriate, evidence-based treatment options if necessary. These might include topical treatments like Minoxidil, oral medications like Finasteride (primarily for male AGA), Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), or hair transplantation in some cases. The AAD offers information on diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion: Vaping and Hair Loss – Correlation vs. Causation
So, does vaping directly cause hair loss? Currently, there is **no definitive scientific proof** establishing a direct causal link specifically between vaping and common forms of hair loss like androgenetic alopecia. However, plausible biological mechanisms exist through which components of vaping – primarily nicotine’s effect on blood flow and potentially oxidative stress from aerosol constituents – *could* negatively influence the hair growth cycle or exacerbate existing tendencies towards hair thinning.
Compared to traditional smoking, which has a more established link to hair loss due to its far greater toxic burden, vaping is considered less harmful. Yet, it’s not risk-free. Anecdotal reports from some vapers suggest perceived changes in hair health, warranting further investigation.
Ultimately, hair health reflects overall well-being. While the specific role of vaping remains under investigation, focusing on a healthy lifestyle – balanced nutrition, stress management, adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking – provides the best foundation for healthy hair. If you are concerned about hair loss, whether you vape or not, seeking professional medical advice from a doctor or dermatologist is the most reliable way to get an accurate diagnosis and discuss effective management strategies tailored to your individual situation.
- HHC Vapes: What Are They & Are They Safe? - July 31, 2025
- Cannabis and Vape Shop Workers Rank Happiest in Nation - July 31, 2025
- Richmond, VA, Restricts New Vape & Tobacco Shop Locations - July 31, 2025







