The Truth About Vaping: Understanding the Facts and Statistics
Vaping has become a common way for people to inhale vaporized substances, often including nicotine. The vaping industry has been rapidly expanding in recent years, introducing new products and devices on a regular basis. This article will take a closer look at the statistics of the vaping worldwide, the main reasons people choose to vape, the regulations and policies that govern it, and the potential health risks associated with it.
Definition of Vaping
Vaping is the act of inhaling vaporized substances through an electronic device, commonly known as an e-cigarette or vape pen. These devices work by heating a liquid, called e-juice or e-liquid, which typically contains nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals.
Overview of the Vaping Industry
The vaping industry has experienced rapid growth in recent years. According to Grand View Research, the global vaping market size was valued at $15.04 billion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.8% from 2021 to 2028. The market is driven by the growing popularity of e-cigarettes, increasing demand for flavored e-liquids, and the shift from traditional smoking to vaping.
How Popular is Vaping?
Overview
Vaping has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly among young adults and teenagers. In the United States, the number of high school students who reported using e-cigarettes increased from 1.5% in 2011 to 27.5% in 2019, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Vaping Statistics in the U.S.
In the United States, there are currently an estimated 10.8 million adult e-cigarette users, according to data from the National Health Interview Survey. Additionally, the CDC reports that in 2020, about 19.6% of adults aged 18–24 years reported using e-cigarettes, and 9.1% of adults aged 25–44 years reported using them.
| Statistics | Source |
|---|---|
| Youth e-cigarette use rose 1,800% from 2011 to 2019 | Truth Initiative, 2019 |
| Two-thirds of young JUUL users (ages 15 to 21) don’t know that the product always contains nicotine | Truth Initiative, 2019 |
| In 2019, 10.5% of middle school students reported using vaping products within the past month | CDC, 2019 |
| Around 61% of teens who vape do it “to experiment,” 42% because they like the taste, 38% to have a good time, 37% to relieve tension, and 29% to feel good or get high | Monitoring the Future, 2019 |
Vaping Statistics Worldwide
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there are more than 41 million vapers worldwide. The Asia Pacific region is the largest market for e-cigarettes, accounting for over 40% of the global market share.
| Statistics | Source |
|---|---|
| In 2011, there were 7 million e-cigarette users worldwide. By 2018, that number had increased to 41 million. | World Health Organization, 2018 |
| There will be an estimated 55 million e-cigarette users worldwide by 2021. | Euromonitor, 2018 |
| Worldwide vaping sales reached $15.7 billion in 2018 and they’re expected to reach $40 billion by 2023. | The Lancet, 2019 |
| The three largest markets for vaping products are the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan. | Euromonitor, 2018 |
Vaping Statistics by Age
Vaping is most common among young adults and teenagers. According to a survey conducted by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, about 25% of 12th graders in the United States reported using e-cigarettes in the past 30 days. Additionally, the survey found that 5.7% of middle school students and 27.5% of high school students reported using e-cigarettes in the past 30 days.
| Statistics | Source |
|---|---|
| 20% of Americans ages 18 to 29 use vape products, compared with 16% of those ages 30 to 64, and fewer than 0.5% among those 65 and older. | Gallup, 2018 |
| Young people ages 15 to 17 are 16 times more likely to vape than people age 25 to 34. | Truth Initiative, 2018 |
| From 2017 to 2019, the percent of high school students who vaped in the past 30 days increased among 12th graders (11% to 25%), 10th graders (8% to 20%), and 8th graders (4% to 9%). | The New England Journal of Medicine, 2019 |
Teen Vaping Statistics
Teen vaping is a major concern for public health officials, as it can lead to nicotine addiction and other health risks. According to the CDC, in 2020, 19.6% of high school students and 4.7% of middle school students reported using e-cigarettes.
| Statistics | Source |
|---|---|
| Youth e-cigarette use rose 1,800% from 2011 to 2019. | Truth Initiative, 2019 |
| Two-thirds of young JUUL users (ages 15 to 21) don’t know that the product always contains nicotine. | Truth Initiative, 2019 |
| In 2019, 10.5% of middle school students reported using vaping products within the past month. | CDC, 2019 |
| Around 61% of teens who vape do it “to experiment,” 42% because they like the taste, 38% to have a good time, 37% to relieve tension, and 29% to feel good or get high. | Monitoring the Future, 2019 |
Common Reasons for Vaping
There are several reasons why people choose to vape. Some people use e-cigarettes as a way to quit smoking traditional cigarettes, as they believe it is a safer alternative. Others enjoy the different flavors available and the social aspect of vaping. Additionally, some people may use e-cigarettes as a way to self-medicate or as a form of stress relief.
| Reason for Vaping | Percentage |
|---|---|
| To see what it’s like | 60.9% |
| Because they like how it tastes | 41.7% |
| As a social activity | 37.9% |
| To relax | 37.4% |
| To feel good or get high | 29.0% |
| They’re bored | 28.7% |
| Because they think it looks cool | 15.2% |
| They have an addiction | 8.1% |
| To help quit regular cigarettes | 6.1% |
The pecuniary cost of vaping
Despite being deemed as a cheaper alternative to the conventional cigarette, should not be taken lightly. In truth, it is quite an expensive habit to maintain, with a range of $387 to $5,082.50 yearly as compared to the expenses incurred by smoking one pack of cigarettes per diem, which can cost $2,087.80 to $5,091.75, as stated by Ruthless Vapor, the eliquid manufacturer.
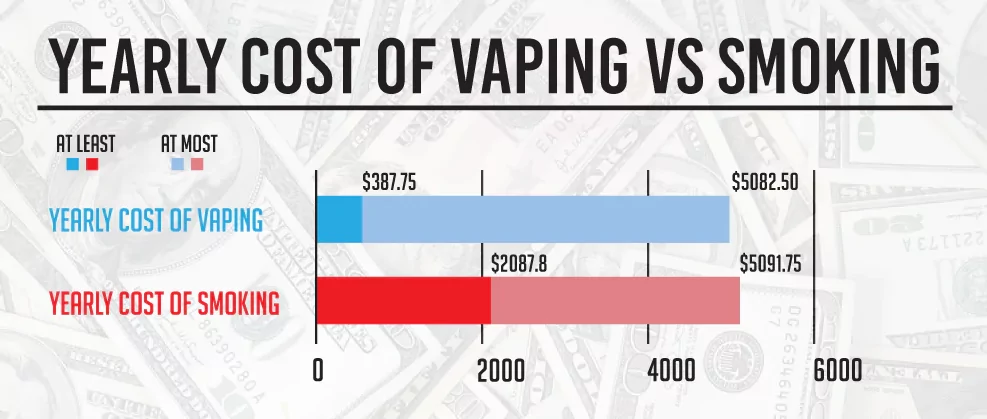
Based on reports, the global sales of e-cigarettes and other related vaping products are anticipated to reach over $40 billion in the year 2023. The median cost for regular e-cigarette users amounts to $50 to $75 per month, and at times, can go as high as $250 per month, according to the Tobacco Prevention and Cessation organization in 2016.
In the year 2017, an emergency room visit amounted to an average cost of $1,389. It should be noted that the amount cited is inclusive of visits for all reasons and not just those that are related to vaping. Meanwhile, a three-day stay in a hospital can set one back by $30,000, although the cost quoted is the average expense of any hospital stay, not particularly those associated with vaping.
Vaping regulations and policies
As vaping gained popularity, regulators began to take notice and develop policies around its use. At the federal level, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the manufacturing, distribution, and marketing of e-cigarettes and other vaping products. In 2016, the FDA extended its regulatory authority to cover e-cigarettes, which means that manufacturers must submit their products for review to determine whether they are appropriate for public use.
One of the biggest issues surrounding vaping is its use among minors. In an effort to curb underage vaping, the FDA implemented regulations that require manufacturers to include a health warning on their products and prohibit the sale of e-cigarettes to anyone under 18 years of age. Additionally, the sale of flavored e-cigarettes, which are often seen as more appealing to younger users, was banned in 2020.
In addition to federal regulations, state and local governments have also taken steps to regulate the use of e-cigarettes. As of 2021, 20 states and the District of Columbia have banned the use of e-cigarettes in workplaces, restaurants, and other public spaces. Some states have also implemented taxes on e-cigarette sales as a way to discourage use.
It’s important to note that regulations and policies around vaping are constantly evolving as more research is conducted on the health effects of e-cigarette use. While some argue that vaping is a safer alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes, others are concerned about the potential long-term health risks associated with vaping.
Health risks associated with vaping
While vaping may be seen by some as a healthier alternative to smoking, it still poses significant health risks. One of the biggest risks associated with vaping is nicotine addiction. E-cigarettes often contain high levels of nicotine, which can lead to addiction and have negative effects on brain development, particularly in adolescents.
In addition to nicotine addiction, vaping has been linked to respiratory issues, including lung damage and respiratory failure. Vaping can also cause inflammation and damage to blood vessels, which can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues.
Another concern with vaping is the potential for harmful chemicals to be released during the heating of e-liquid. While e-cigarettes don’t contain the same harmful chemicals found in traditional cigarettes, they still contain other chemicals that can be harmful when heated and inhaled. Studies have shown that some of these chemicals can cause cancer and other serious health issues.
Conclusion
Vaping has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly among younger individuals. While it may be seen as a safer alternative to smoking, it still poses significant health risks and can be addictive. As regulations and policies around vaping continue to evolve, it’s important for individuals to be aware of the potential risks and make informed decisions about their use of e-cigarettes.
It’s also important for policymakers and healthcare professionals to continue to conduct research on the health effects of vaping and develop effective strategies for regulating its use. By working together, we can ensure that individuals are able to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, while also protecting public health and safety.
Related vaping research:
- What percentage of Americans vape?, Gallup
- Vaping facts, stats, and regulations, Truth Initiative
- The impact of e-cigarettes on the lung, American Lung Association
- Teens and e-cigarettes, National Institute on Drug Abuse
- Before recent outbreak, vaping was on the rise in U.S., especially among young people, Pew Research Center
- Quick facts on the risks of e-cigarettes for kids, teens, and young adults, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Know the risks: e-cigarettes and young people, Surgeon General
- Youth tobacco use: Results from the national youth tobacco survey, U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Trends in adolescent vaping, 2017-2019, The New England Journal of Medicine
- New study reveals teens 16 times more likely to use JUUL than older age groups, Truth Initiative
- Prevalence and distribution of e-cigarette use among U.S. adults, Annals of Internal Medicine
- Vaping: a growing global health concern, The Lancet
- A dollars and “sense” exploration of vape shop spending and e-cigarette use, Tobacco Prevention and Cessation
- Electronic-cigarette smoke induces lung adenocarcinoma and bladder urothelial hyperplasia in mice, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
- 10 years of emergency room spending for the commercially insured, Health Care Cost Institute
- Protection from high medical costs, Healthcare.gov
- Most expensive health conditions in the U.S., Business Insider
- Bestselling Vapes in UK After Disposable Ban: What to Stock 2025 - August 8, 2025
- Argentina Debates Stricter Vape Laws Amid Prohibition Failures - August 8, 2025
- Nigeria Advocacy Group Urged to Hike Tobacco & Vape Tax by 100% - August 8, 2025









